Gellan gum is a watersoluble anionic exopolysaccharide made through refinement, drying and grinding after pure cultivation and fermentation of carbohydrate with pseudomonas elodea.
The main chain of Gellan gum polysaccharide is a linear tetrasccharide repeating unit, including (1→3)-D-glucose, β(1→4)-D-glucuronic acid, β(1→4)-D-glucose, and α(1→4)-L-rhamnose. Basically, there are two types of commercial gellan gums: naturally extracted gellan gum and low-acyl gellan gum. Naturally extracted gellan gum is also called high-acyl gellan gum. Its molecular structure includes the main chain composed of tetrasccharide repeating units and also includes branched chain groups. There is a glyceroyl at the location of C-3 of the first glucosyl group. There is an acetyl at the location of C-6 on the other half of the same glucosyl group. The low-acyl gellan gum is the product of natural gellan gum after the acetyl and glyceroyl are removed.
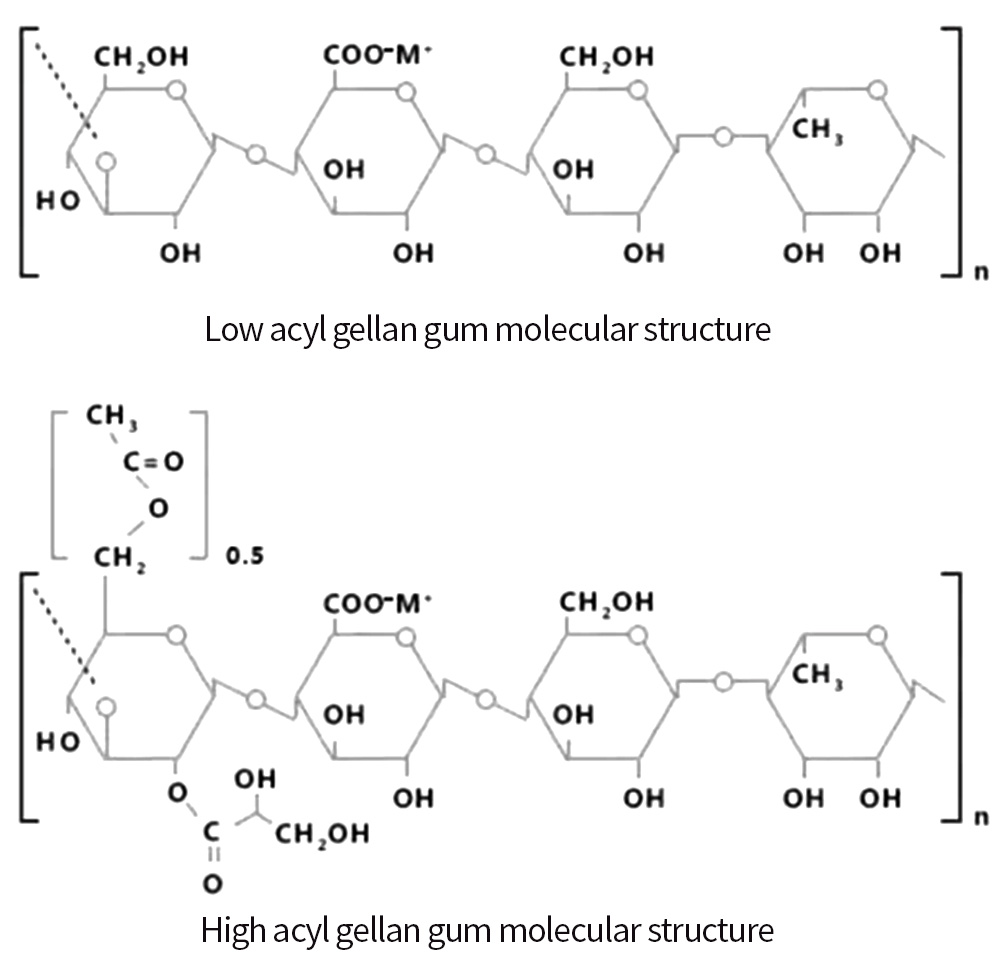
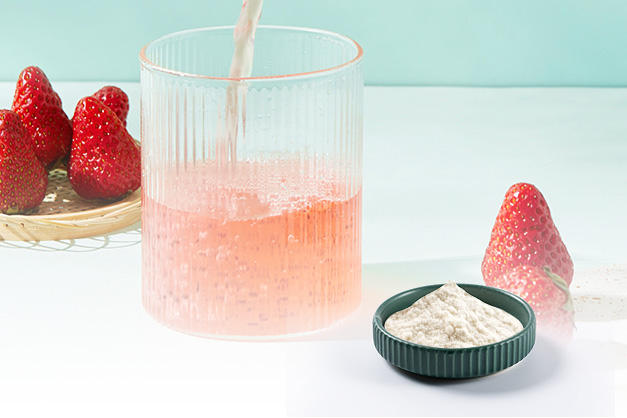
Gellan gum has been widely applied to food, pharmaceutical, chemical and many other fields as the emulsifier, suspending agent, thickener, stabilizer, gel, film forming agent and lubricant. It has been one of the most prospective microbial polysaccharides in recent years.
BLG selects excellent bacterial species and carbon sources, phosphate, organic and inorganic nitrogen sources as well as a proper amount of trace elements, adopts advanced fermentation and extraction process and strict quality management and develops application solutions of gellan gum in fields like dairy drinks, jelly and pudding, candies, daily chemical and pet foods to meet different demands of customers.



